二分查找
二分查找也称折半查找(Binary Search),它是一种效率较高的查找方法。但是,折半查找要求线性表必须采用顺序存储结构,而且表中元素按关键字有序排列。
基本思想
首先,假设表中元素是按升序排列,将表中间位置记录的关键字与查找关键字比较,如果两者相等,则查找成功;否则利用中间位置记录将表分成前、后两个部分,如果中间位置记录的关键字大于查找关键字,则在后半部分中继续查找,否则在前半部分中查找。重复以上过程,直到找到满足条件的记录,使查找成功,或查找完整个表,此时查找不成功。
算法实现
package com.zys.search;
/**
* @program: dataStructure
* @description: 折半查找(二分查找)
* @author: Leo
* @create: 2019-05-16 17:26
**/
public class BinarySearch {
/**
* 二分查找(非递归实现)
* @Description: 返回key在arr中的索引 不存在则返回-1
* @Param: [arr, key] 数组必须有序
* @return: int
* @Author: Leo
*/
public static int binarySearchNoRecursion(int[] arr,int key){
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high){
//int mid = (low + high) / 2;
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;//防溢出
if (key == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}else if (key < arr[mid]){
high = mid - 1;
}else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 二分查找(递归实现)
* @Description: 返回key在arry中的索引 不存在则返回-1
* @Param: [arr, key] 数组必须有序
* @return: int
* @Author: Leo
*/
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int key) {
return binarySearch(arr, key, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
private static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int key, int low, int high) {
if (low > high)
return -1;
//int mid = (low + high) / 2;
int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;//防溢出
if (key == arr[mid]) {
return mid;
} else if (key < arr[mid]) {
return binarySearch(arr, key, low, mid - 1);
} else {//key > arr[mid]
return binarySearch(arr, key, mid + 1, high);
}
}
}
插值查找
插值查找,有序表的一种查找方式。插值查找是根据查找关键子与查找表中最大最小记录关键字比较后的查找方法。插值查找基于二分查找,将查找点的选择改进为自适应选择,提高查找效率。
基本思想
插值查找基本思想和二分查找相同,只是插值查找将查找点的选择加入了对查找值的考虑,即从mid = (left + right) / 2,更安全的做法是mid = left + (right - left) / 2,改为了mid = left + (right - left) * (key - arr[left]) / (arr[right] - arr[left])其中arr即为有序数组。使得在数组数据量较大,关键字分布比较均匀时能够更快的定位到查找值的索引。
算法实现
package com.zys.search;
/**
* @program: dataStructure
* @description: 插值查找(对于数据量较大,关键字分布比较均匀时速度较快)
* @author: Leo
* @create: 2019-08-02 14:14
**/
public class InterpolationSearch {
/**
* 插值查找(递归实现)
*
* @param arr 有序数组(这里是升序,如果是降序,修改部分比较语句即可)
* @param key 要查找的值
* @return 返回查找到的值在数组中的索引(不存在返回-1)
*/
public static int interpolationSearch(int[] arr, int key) {
return interpolationSearch(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, key);
}
private static int interpolationSearch(int[] arr, int left, int right, int key) {
//不符合条件,返回-1
//条件key < arr[left] || key > arr[right]不仅能快速得出key不在数组范围内
//也防止了在计算中间索引时越界
if (left > right || key < arr[left] || key > arr[right]) {
return -1;
}
//计算中间索引(和二分查找主要的区别,根据key自适应查找位置)
int mid = left + (right - left) * (key - arr[left]) / (arr[right] - arr[left]);
if (key > arr[mid]) { //向右递归查找
return interpolationSearch(arr, mid + 1, right, key);
} else if (key < arr[mid]) { //向左递归查找
return interpolationSearch(arr, left, mid - 1, key);
} else { //查找到了,返回索引
return mid;
}
}
/**
* 插值查找(非递归实现)
* @param arr
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static int interpolationSearchNoRecursion(int[] arr, int key) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
//不符合条件,返回-1
//条件key < arr[left] || key > arr[right]不仅能快速得出key不在数组范围内
//也防止了在计算中间索引时越界
if (left > right || key < arr[left] || key > arr[right]) {
return -1;
}
while (left <= right) {
//计算中间索引(和二分查找主要的区别,根据key自适应查找位置)
int mid = left + (right - left) * (key - arr[left]) / (arr[right] - arr[left]);
if (key > arr[mid]) { //向右查找
left = mid + 1;
} else if (key < arr[mid]) { //向左查找
right = mid - 1;
} else { //查找到了,返回索引
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
斐波那契(黄金分割)查找
斐波那契查找就是在二分查找的基础上根据斐波那契数列进行分割的。
基本思想
在斐波那契数列找一个等于略大于查找表中元素个数的数F(k),将原查找表扩展为长度为F(k)(如果要补充元素,则补充重复最后一个元素,直到满足F(k)个元素),完成后进行斐波那契分割,即F(k)个元素分割为前半部分F(k)个元素,后半部分F(k)个元素,根据和黄金分割点的比较结果继续在某个部分里查找,直到找到或找完整个表。
图解
算法实现
package com.zys.search;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @program: dataStructure
* @description: 斐波那契查找
* @author: Leo
* @create: 2019-08-02 15:08
**/
public class FibonacciSearch {
//斐波那契数列大小
private static final int maxSize = 20;
/**
* 斐波那契查找(非递归实现)
*
* @param arr 有序数组
* @param key 待查找的值
* @return 待查找的值在数组中的索引(不存在返回-1)
*/
public static int fibonacciSearch(int[] arr, int key) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
//黄金分割点(斐波那契分割点)下标
int mid = 0;
//第一个大于数组长度的斐波那契下标
int k = 0;
//获取斐波那契数列
int[] fibSeq = getFibonacciSeq(maxSize);
//找到第一个大于数组长度的斐波那契下标
while (arr.length > fibSeq[k] - 1) {
k++;
}
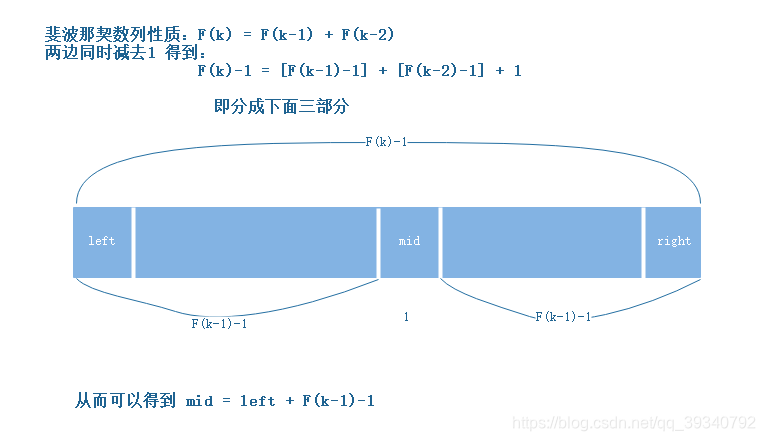
//斐波那契数列性质:F(k) = F(k-1) + F(k-2)
//两边同时减去1 =》 F(k)-1 = (F(k-1)-1) + (F(k-2)-1) + 1,其中等式右边最后1表示我们需要找的mid的位置,
//那么数组被分为 两部分 =》 左:F(k-1)-1 右:F(k-2)-1 从而可以计算出分割点下标=》 mid = left + F(k-1)-1
//由于fibSeq[k](斐波那契数列第k项-1) 可能大于数组长度, 所以需要新建一个临时数组,扩容至fibSeq[k]大小
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(arr, fibSeq[k]);
//将扩容后数组 自动填充的部分用原数组最后一个值填充
for (int i = right + 1; i < temp.length; i++) {
temp[i] = arr[right];
}
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + fibSeq[k - 1] - 1;
if (key > temp[mid]) { //向右查找
left = mid + 1;
// F(k) = F(k-1) + F(k-2) ,此时需要向右查找,右边部分长度为F(k-2)
// 继续分割 =》 F(k-2) = F(k-3) + F(k-4),即下一次在F(k-4)那部分中继续查找
k -= 2;
} else if (key < temp[mid]) { //向左查找
right = mid - 1;
// F(k) = F(k-1) + F(k-2) ,此时需要向左查找,左边部分长度为F(k-1)
// 继续分割 =》 F(k-1) = F(k-2) + F(k-3),即下一次在F(k-2)那部分中继续查找
k--;
} else { //找到了
//判断mid是在原数组范围内还是扩充后的范围内
if (mid <= arr.length - 1) { //在原数组范围内
return mid;
} else { //在扩充后的范围内(即为原数组最后一个值,返回数组最后一个索引即可)
return arr.length - 1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 获取斐波那契数列
*
* @param size 斐波那契数列大小
* @return
*/
private static int[] getFibonacciSeq(int size) {
if (size <= 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("斐波那契数列大小 " + size + " 不合法");
}
int[] temp = new int[size];
temp[0] = 1;
temp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < size; i++) {
temp[i] = temp[i - 1] + temp[i - 2];
}
return temp;
}
}
简单测试(JUnit)
package com.zys.test;
import com.zys.search.BinarySearch;
import com.zys.search.FibonacciSearch;
import com.zys.search.InterpolationSearch;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @program: dataStructure
* @description: 查找测试类
* @author: Leo
* @create: 2019-05-16 17:09
**/
public class SearchTest {
private int[] arr;
@Before
public void createArr() {
//初始化有序数组
arr = new int[]{12, 24, 38, 43, 56, 66, 78, 87, 98, 100};
}
@Test
public void testBinarySearch() {
int key = 66;
//int index = BinarySearch.binarySearch(arr, key);
int index = BinarySearch.binarySearchNoRecursion(arr,key);
if (index != -1)
System.out.println(key + " 在数组中的索引为 " + index);
else
System.out.println("数组中不存在 " + key);
}
@Test
public void testInterpolationSearch() {
int key = 78;
//int index = InterpolationSearch.interpolationSearch(arr, key);
int index = InterpolationSearch.interpolationSearchNoRecursion(arr, key);
if (index != -1)
System.out.println(key + " 在数组中的索引为 " + index);
else
System.out.println("数组中不存在 " + key);
}
@Test
public void testFibonacciSearch() {
int key = 66;
int index = FibonacciSearch.fibonacciSearch(arr,key);
if (index != -1)
System.out.println(key + " 在数组中的索引为 " + index);
else
System.out.println("数组中不存在 " + key);
}
}



